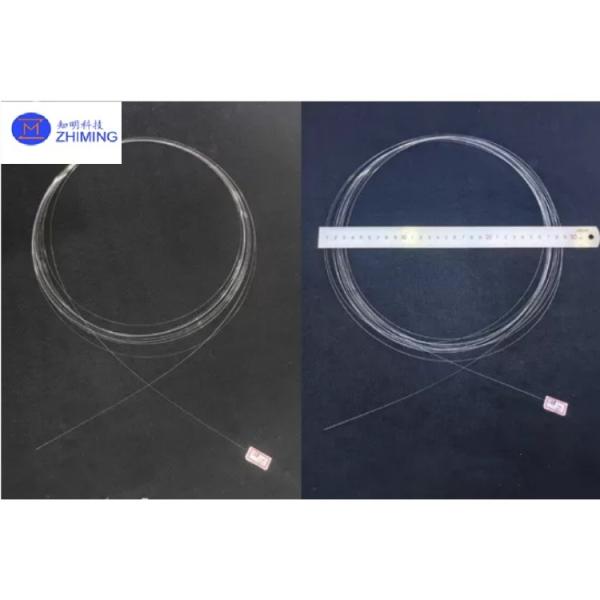
Sapphire Fiber Al2O3 single crystal transparent crystal optical
cable optical fiber communication line 25-500um
Character of Sapphire Fiber
- Support customized designs with artwork specifications.
- Made from synthetic sapphire (99.999% Al2O3).
- High performance with a hardness rating of 9.0, offering
excellent wear resistance.
- 85% light transmissivity for optimal visibility.
- Widely used in high-tech applications, including smartphone
screens, watch crystals, high-durability
components, and optical windows.
Description of Sapphire Fiber
Sapphire is a chemically and scratch-resistant material with a
melting point of 2,072°C. MMI offers LHPG-grade sapphire fibers
with diameters from 25 to 500 μm. In addition, fibers are available
with an extended end through a tapered end. This is an important
feature because the flexibility of the fiber is inversely
proportional to the 4th power of the diameter (e.g., a 100 μm fiber
is 16 times more flexible than a 200 μm fiber). Tapered fiber
provides users with high throughput capability without sacrificing
flexibility in energy transmission and spectroscopy applications.
PTFE sheaths and/or connectors can be used for fibers larger than
100 μm in diameter.
More Details of Sapphire Rod
| Chemical formula | Al2O3 |
| Crystal class | Hexagonal system, rhomboidal class 3m |
| Density, g/cm3 | 3.98 |
| Melting point, °K | 2303 |
| Optical transmission range, µm | 0.17 - 5.5 |
| Refractive index at 0.532 µm | n0=1.7717, ne=1.76355 |
| Water absorption | nil |
| Young Modulus, Gpa | 345 |
| Shear Modulus, Gpa | 145 |
| Bulk Modulus, Gpa | 240 |
Key features:
High temperature resistance: Sapphire fibers can operate at
temperatures up to 2000°C without damage or degradation, making
them particularly suitable for high-temperature environments.
Chemical Stability: Sapphire materials are highly resistant to most
acids, bases, and other chemicals, ensuring their stability even in
challenging chemical environments.
Mechanical strength: Sapphire fibers have high mechanical strength
and excellent abrasion and impact resistance.
Optical transparency: Due to the purity of its material, sapphire
fibers have a high degree of transparency in the visible and
near-infrared regions.

- Wide bandwidth: Sapphire fibers are capable of transmitting optical
signals over a wide range of wavelengths.
- Biocompatible: Sapphire fibers are harmless to most biological
entities, making them particularly useful in medical applications.
- Radiation resistance: For some nuclear applications, sapphire
fibers exhibit good radiation resistance.
- Long service life: Due to their abrasion resistance and chemical
stability, sapphire fibers have a long service life in many
applications.
- These characteristics make sapphire fibers ideal for a variety of
high-end and challenging applications, including sensing, medical
imaging, pyrometry, and nuclear applications.
Applications:
- High-temperature sensing: Due to their resistance to high
temperatures, sapphire fibers are used as fiber optic sensors in
high-temperature environments, such as in steel production or
aerospace engine testing.
- Medical imaging and treatment: The optical clarity and
biocompatibility of sapphire fibers make them popular in endoscopy,
laser therapy, and other medical applications.
- Chemical and biosensing: Due to its chemical stability, sapphire
fibers are used in chemical and biological sensors that require
corrosion resistance.
- Nuclear industry applications: The radiation-resistant properties
of sapphire fibers allow them to be used for monitoring nuclear
power plants and other radioactive environments.

- Optical communication: In some specific applications, sapphire
fibers are used for data transmission, especially when high
bandwidth and fast transmission rates are required.
- Industrial heating and heating furnaces: In high-temperature
furnaces and other heating equipment, sapphire fiber optics are
used as sensors to monitor equipment temperatures and conditions.
- Laser applications: Sapphire fibers can be used to transmit
high-power lasers, e.g. for industrial cutting or medical
treatment.
- R&D: In research laboratories, sapphire fibers are used in a
variety of experiments and measurements, including those carried
out in extreme environments.
These applications are just the tip of the iceberg of the potential
uses for sapphire fibers. With the advancement of technology, its
application field may be further expanded.
About us
Our enterprise, ZMSH, specialises in the research, production,
processing, and sales of Semiconductor substrates and optical
crystal materials.
We have an experienced engineering team, management expertise,
precision processing equipment, and testing instruments, providing
us with extremely strong capabilities in processing non-standard
products.
We can research, develop, and design various new products according
to customer needs.
The company will adhere to the principle of "customer-centred,
quality-based" and strive to become a top-tier high-tech enterprise
in the field of optoelectronic materials.
FAQ
1. Q: Are sapphire fibers easy to break?
A: Sapphire is a brittle material. Although it has high hardness,
it may break when subjected to strong impact or bending.
2. Q: Are the sapphire fibers widely applicable?
A: Sapphire needles are widely used in the following fields:
Electronics industry, optoelectronic equipment, mechanical parts,
medical devices